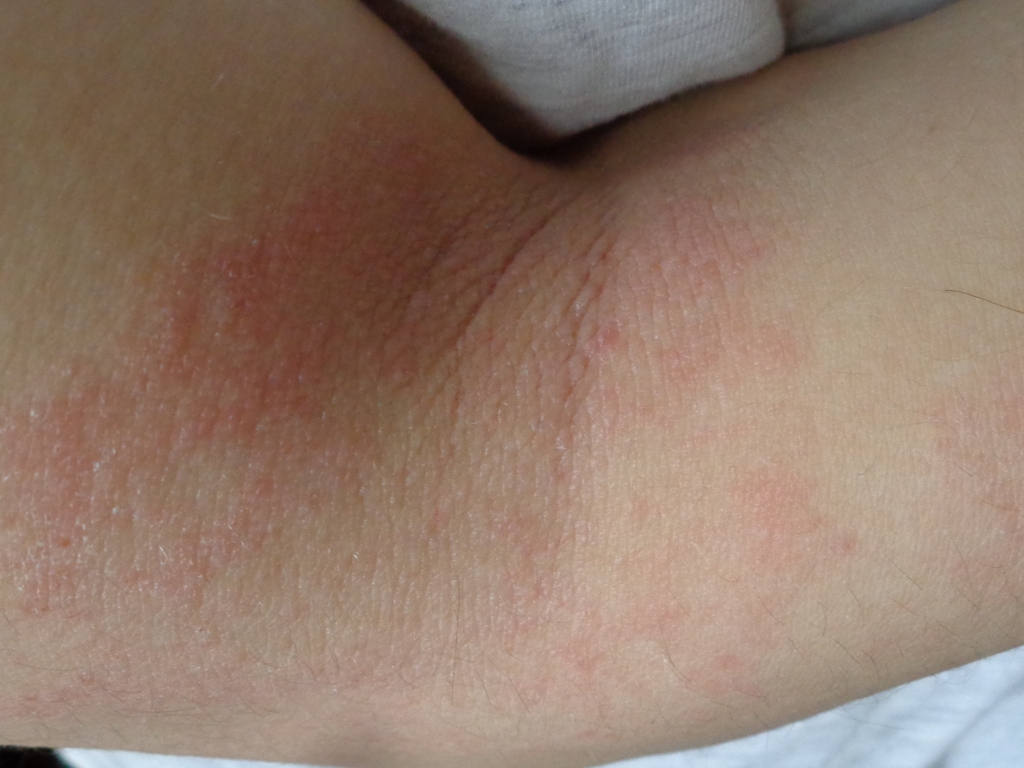
Atopic Dermatitis: Understanding, Managing, and Treating
Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that causes the skin to become itchy, red, and swollen. The condition is prevalent in infants and children but can persist into adulthood. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the causes, symptoms, diagnostic procedures, treatment options, and preventive strategies for atopic dermatitis.
What is Atopic Dermatitis?
Atopic dermatitis is an inflammatory skin condition caused by an abnormal immune response to environmental factors. It is part of the atopic triad, often occurring alongside asthma and allergic rhinitis (hay fever). Eczema affects the skin's barrier function, making it more susceptible to irritants and allergens.
For more information, visit the National Eczema Association.
Who Gets Atopic Dermatitis?
Atopic dermatitis commonly affects infants and children, with symptoms often appearing within the first year of life. However, it can also commence during adolescence or adulthood. Risk factors include:
- Family history of eczema, asthma, or allergies.
- Living in an urban environment.
- Higher socioeconomic status.
How Common is Atopic Dermatitis?
Atopic dermatitis is among the most common skin disorders, affecting approximately 15-20% of children and 1-3% of adults worldwide. It is a significant public health concern due to its association with other atopic conditions and its impact on quality of life.
Symptoms and Causes
What are the Signs of Atopic Dermatitis?
Symptoms can vary with age and individual cases but generally include:
- Intense Itching: Especially at night, leading to scratching and further irritation.
- Red to Brownish-Gray Patches: Often present on the hands, feet, ankles, wrists, neck, upper chest, eyelids, and around the eyes.
- Dry, Scaly Skin: The skin may become thickened or leathery over time.
- Small, Raised Bumps: These may leak fluid and form a crust when scratched.
- Raw, Sensitive Skin: Due to repeated scratching and infection.
What Causes Atopic Dermatitis?
Atopic dermatitis arises from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. It involves:
- Genetic Mutations: Mutations in the filaggrin gene that code for proteins necessary in maintaining skin's barrier.
- Immune System Dysregulation: Hyper-reactive immune responses to allergens and irritants.
- Environmental Triggers: Contact with specific allergens, stress, weather changes, and infections can exacerbate symptoms.
Diagnosis and Tests
How is Atopic Dermatitis Diagnosed?
Diagnosis is primarily based on clinical examination and patient history. Key diagnostic features include:
- Physical Examination: Observing skin appearance and distribution of rashes.
- Patient History: Considering family history of atopy, frequency, duration, and triggers of flares.
- Patch Testing: To rule out contact allergies.
- Skin Biopsy: In unusual cases, to confirm diagnosis by ruling out other conditions.
Management and Treatment
How is Atopic Dermatitis Treated?
Effective management involves a combination of lifestyle changes, skincare routines, and medication:
Emollients and Moisturizers
Application of emollients reduces moisture loss and helps repair the skin barrier. Recommended products include:
Topical Corticosteroids
These are the cornerstone of atopic dermatitis treatment to reduce inflammation. Examples include:
- Hydrocortisone cream (available OTC)
- Triamcinolone acetonide (prescription)
Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors
These non-steroidal medications like tacrolimus (Protopic®) and pimecrolimus (Elidel®) are useful for sensitive skin areas.
Antihistamines
Oral antihistamines may help relieve itching, especially at night.
Systemic Therapies
In severe cases, systemic immunomodulators or biologics like dupilumab (Dupixent®) may be necessary.
For a comprehensive list of medications, visit MedlinePlus.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
- Bathe Regularly: Use lukewarm water and hypoallergenic soap.
- Apply Moisturizers Immediately Post-Bath: This helps trap moisture.
- Avoid Triggers: Identify and avoid exposure to allergens and irritants.
- Wear Soft, Breathable Fabrics: Cotton is preferred over wool or synthetic materials.
Prevention
Preventive measures to reduce the frequency of flare-ups include:
- Maintaining Skin Hydration: Consistent use of emollients.
- Allergen Avoidance: Awareness and avoidance of environmental triggers.
- Stress Management: Implement stress-reduction techniques like yoga and meditation.
Outlook / Prognosis
While atopic dermatitis can be a chronic condition, treatment can control symptoms and improve quality of life. Many children outgrow the condition, but some continue to experience it into adulthood.
Living With Atopic Dermatitis
When Should I Call the Doctor?
Consult a healthcare provider if:
- Symptoms persist despite treatment.
- The skin appears infected (pus, redness, or swelling).
- The condition severely impacts daily activities or sleep.
- You are pregnant and unsure about the safety of medications.
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor?
- What triggers should I be aware of and avoid?
- What is the best skincare regimen for me?
- How can I manage flares at home?
- Are there any new treatments available?
Additional Common Questions
Is Atopic Dermatitis Contagious?
No, atopic dermatitis is not contagious. You cannot contract it through contact with another person.
Can Diet Affect Atopic Dermatitis?
While not a direct cause, certain foods may exacerbate symptoms in some individuals. An elimination diet may help identify potential food allergens.
For additional resources and support, visit the American Academy of Dermatology or Cleveland Clinic.
By understanding atopic dermatitis and working with a healthcare provider, individuals can effectively manage the condition and minimize its impact on daily life.
Identify Skin Conditions Instantly
Try Rash ID for Free