.jpg?)
Heat Rash (Miliaria)
Heat Rash (Miliaria): Understanding, Prevention, and Treatment
Heat rash, also known as miliaria, is a common condition that occurs when the sweat glands become blocked and sweat is trapped under the skin. This skin issue is prevalent in hot, humid climates but can affect anyone, especially if they are prone to sweating. It can lead to discomfort due to its itchy and prickly nature.
Types of Heat Rash
There are several types of miliaria, each varying in severity:
- Miliaria Crystallina: The mildest form, appearing as clear, fluid-filled blisters and bumps on the skin. It is more common in young babies than adults and typically causes no discomfort.
- Miliaria Rubra: Known as 'prickly heat,' this form causes red bumps and intense itching or prickling. It results from deeper blockage in the sweat ducts and may lead to less sweating, causing discomfort.
- Miliaria Profunda: A less common form that can recur chronically, appearing as flesh-colored lesions resembling goosebumps. It's the result of sweat leaking into deeper layers of skin.
- Miliaria Pustulosa: A complicated form where pustules may form, indicating inflammation.
Identifying Heat Rash: Symptoms
Understanding the symptoms of heat rash can aid in timely identification and management:
- Tiny, Red Bumps or Blisters: Particularly on skin folds or areas where sweat accumulates.
- Itching or Prickling Sensation: Intensifies when affected skin is warmed.
- Slight Swelling ("Milky White Swelling"): May be present, causing discomfort.
- Lack of Sweating in Affected Areas: Especially in miliaria rubra and profunda.
Who Gets Heat Rash?
While heat rash is common among people of all ages, certain factors increase your risk:
- Hot, Humid Weather: Particularly common in the summer months.
- Young Infants: Whose sweat ducts are not fully developed.
- Intense Physical Activity: Especially in warm environments.
- Obesity: Increased folds and sweating can raise risk.
- Confinement to Bed: Such as hospitalization, leading to excessive sweating without drying.
Causes of Miliaria
Heat rash occurs when sweat is trapped beneath the skin due to blocked sweat glands. This can be due to:
- Overheating: Environmental heat or tight clothing.
- Excessive Sweating: Contributes to blocked ducts.
- Certain Fabrics: Such as synthetic materials that don’t wick moisture.
- Infectious Agents: Such as bacteria which may block sweat ducts.
Diagnosis and Tests
A healthcare provider can often diagnose heat rash based on the appearance of the rash and a discussion of symptoms and heat exposure. No special tests are typically needed, but severe cases may warrant further examination to rule out infections.
Management and Treatment
If you’re dealing with heat rash, effective management strategies include:
- Cooling Measures: Move to an air-conditioned environment or use fans to minimize sweating.
- Loose Clothing: Wear clothes made from lightweight, breathable fabrics like cotton.
- Cool Baths or Showers: Regular bathing in cool water helps clear ducts.
- Calamine Lotion: Can soothe itching and discomfort on the skin.
- Hydrocortisone Cream: For serious cases, you may consult your healthcare provider about using creams to relieve inflammation.
Medications
- Antihistamines: Mild antihistamines may be advised for itch relief, though consultation with a healthcare provider is recommended.
Home Remedies for Heat Rash
While medical treatment helps, some home remedies may also provide relief:
- Aloe Vera Gel: Known for its soothing properties.
- Cold Compresses: Apply to affected areas for short durations to reduce heat and swelling.
- Avoid Ointments or Oils: These can clog pores, worsening the rash.
Prevention
Preventing heat rash can be achieved through these methods:
- Stay Cool: Use fans or air-conditioning.
- Proper Hydration: Helps regulate body temperature.
- Frequent Showering: Remove sweat and prevent duct blockage.
- Avoid Heavy Creams: On hot days to prevent pore blockage.
Outlook / Prognosis
Miliaria typically resolves without treatment when the skin is cooled and sweat is allowed to evaporate freely from the surface. Chances of recurrence are higher if preventive measures are not taken, particularly during hot weather.
When to See a Doctor
Contact your healthcare provider if:
- Rash Persists: For more than a couple of days.
- Signs of Infection Develop: Such as pus, increased pain, swelling, or redness.
- It's Associated with Fever: Though rare, this may signify a more serious condition.
Additional Common Questions
How long does heat rash last?
Mild heat rash often resolves within hours to a couple of days with cooling and proper skin care.
Can adults get heat rash?
Yes, while infants are more susceptible, adults can also experience heat rash, particularly when exposed to hot, humid conditions or during intense physical activity.
Is heat rash contagious?
No, unlike other skin rashes, miliaria is not contagious and cannot be spread from person to person.
A note from Rash ID's MUM (Medical Understanding AI Model):
Miliaria can be an uncomfortable but usually self-limiting condition. Preventive measures and treatments are typically straightforward and effective. Remember to consult your healthcare provider if standard treatments don’t alleviate symptoms, as they may need to explore other underlying causes.
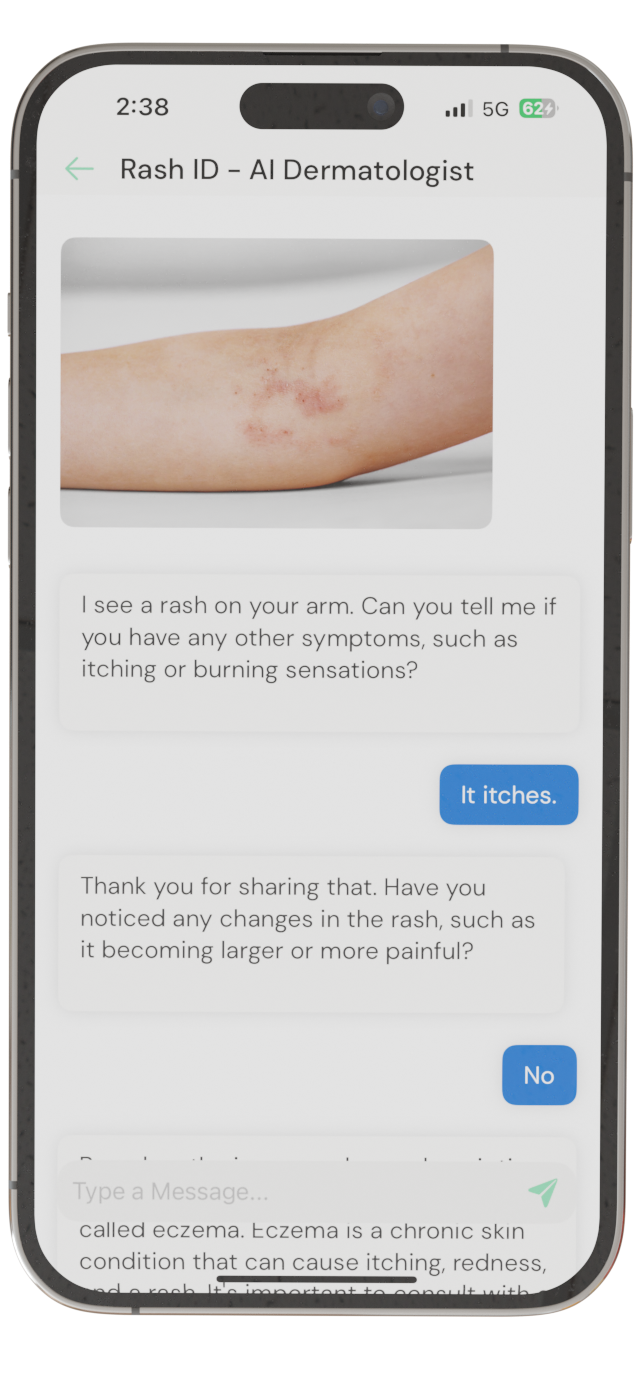
Identify Skin Conditions Instantly
Try Rash ID for Free