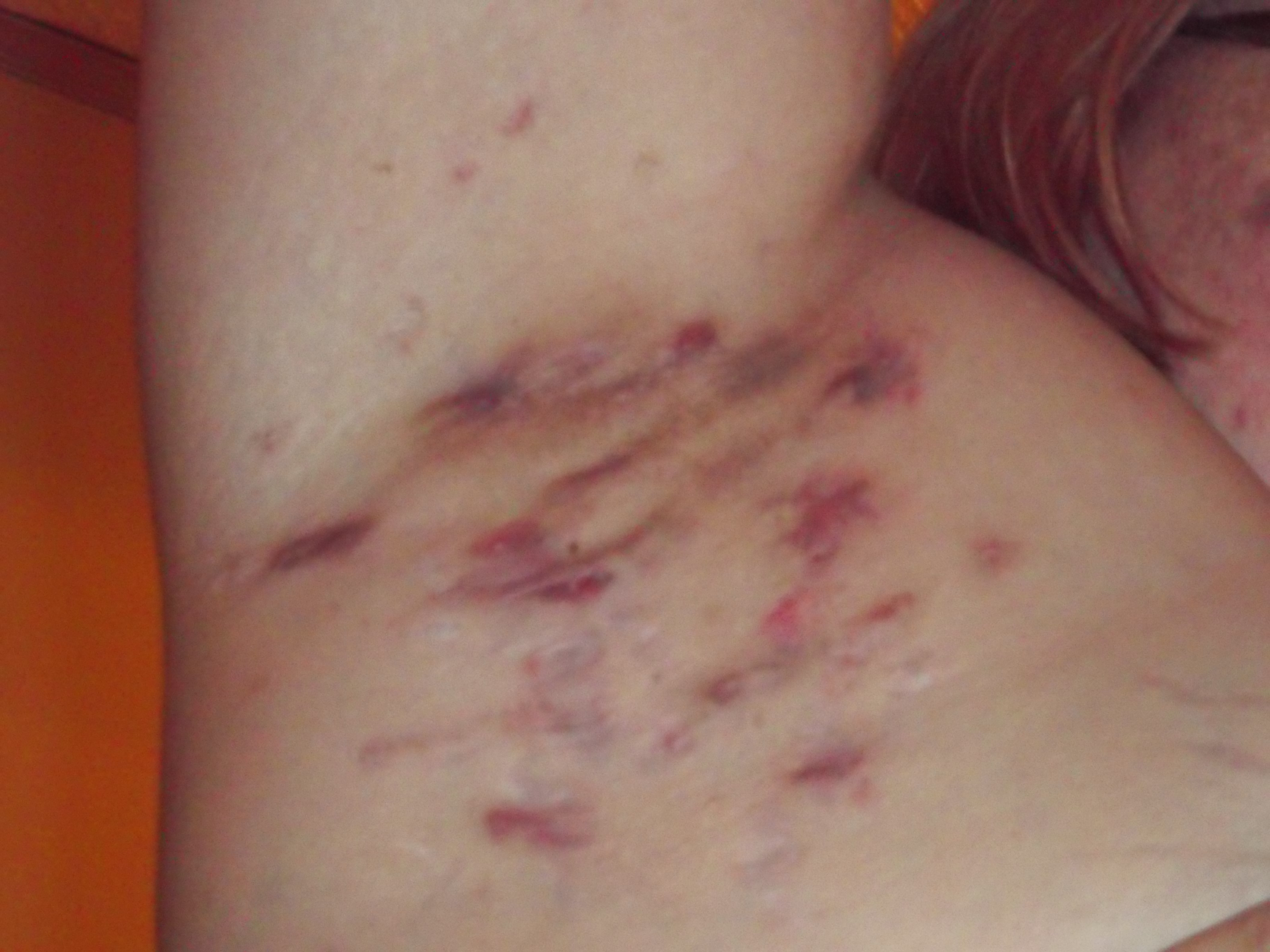
Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Understanding and Managing a Chronic Skin Condition
Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) is a chronic skin condition characterized by the recurrent appearance of painful lumps under the skin, primarily in areas where skin rubs together. Recognizing the significance of early diagnosis and proper management is crucial for individuals affected by this condition.
What is Hidradenitis Suppurativa?
Hidradenitis Suppurativa (commonly abbreviated as HS) is a long-term, recurrent inflammatory skin condition. It is marked by the presence of painful nodules, abscesses, and scarring in areas such as the armpits, groin, buttocks, and under the breasts. These lesions can break open, leading to sinus tracts and tunnels under the skin, causing significant discomfort.
Who is Affected by Hidradenitis Suppurativa?
HS typically begins after puberty and is more common among women and individuals with a family history of the condition. Obesity, smoking, and metabolic syndrome are known risk factors. It is estimated to affect 1% to 4% of individuals, but it's often underreported or misdiagnosed.
Symptoms: How to Recognize Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Hidradenitis Suppurativa varies in severity, and its symptoms can include:
- Painful Nodules: Firm, pea-sized lumps under the skin, which may last for years or flare up periodically.
- Abscess Formation: Fluid-filled nodules that may leak pus and emit a foul odor.
- Scarring and Fibrosis: Repeated inflammation can lead to permanent scarring and thickening of the skin.
- Sinus Tracts: Tunnels that form under the skin, connecting lesions.
Differentiating HS from other conditions like acne or cysts is essential for proper treatment. Read more about symptoms and diagnosis from the Mayo Clinic.
Causes and Pathophysiology
The exact cause of HS is not well understood, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors. It is linked to the blockage of hair follicles, leading to inflammation and infection. Learn about potential genetic factors from the NIH Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center.
Diagnosis and Tests
HS diagnosis is primarily clinical based on patient history and physical examination. In some cases, a healthcare provider may perform a biopsy to rule out other conditions. Review clinical diagnosis criteria from the American Academy of Dermatology.
Management and Treatment
Treating Hidradenitis Suppurativa often requires a comprehensive approach involving lifestyle changes, medications, and sometimes surgical interventions.
Medications:
- Antibiotics: Long-term use of tetracycline antibiotics can help reduce flare-ups.
- Biologics: Medications like adalimumab (Humira®) are specifically approved for HS to reduce immune system activity. Check detailed guidelines on biologic treatments at the HS Foundation.
- Hormonal Therapy: Spironolactone or oral contraceptives can be effective, especially in women.
- Corticosteroids: To manage severe inflammation, though long-term use is not recommended.
Surgical Interventions:
- Incision and Drainage: For immediate relief from painful abscesses.
- Laser Therapy: For hair removal and reduction of lesions.
- Excisional Surgery: Removing affected skin in more severe cases.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies:
- Weight Management: Losing weight can reduce the occurrence of flare-ups.
- Smoking Cessation: Stopping smoking has been shown to improve symptoms significantly.
- Proper Hygiene: Using antiseptic washes to decrease skin irritation.
How to Cope with Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Living with HS can be physically and emotionally challenging. It's crucial to seek support from healthcare providers and connect with others who understand the impact of this condition. Consider joining support groups through the HS Foundation.
FAQs about Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Q: Is HS contagious?
A: No, Hidradenitis Suppurativa is not contagious. It results from genetic and environmental factors, not an infection that spreads.
Q: Can Hidradenitis Suppurativa go away on its own?
A: While symptoms may lessen over time, HS is a chronic condition that typically requires management rather than self-resolution.
Q: Do diet changes help with HS?
A: Some individuals report improvement in symptoms with dietary changes, such as reducing sugar and dairy intake, though evidence is primarily anecdotal.
By understanding Hidradenitis Suppurativa and working with a healthcare professional, individuals can manage symptoms effectively and improve quality of life. For further reading, consult trusted medical resources such as the NIH and NHS portals.
Identify Skin Conditions Instantly
Try Rash ID for Free