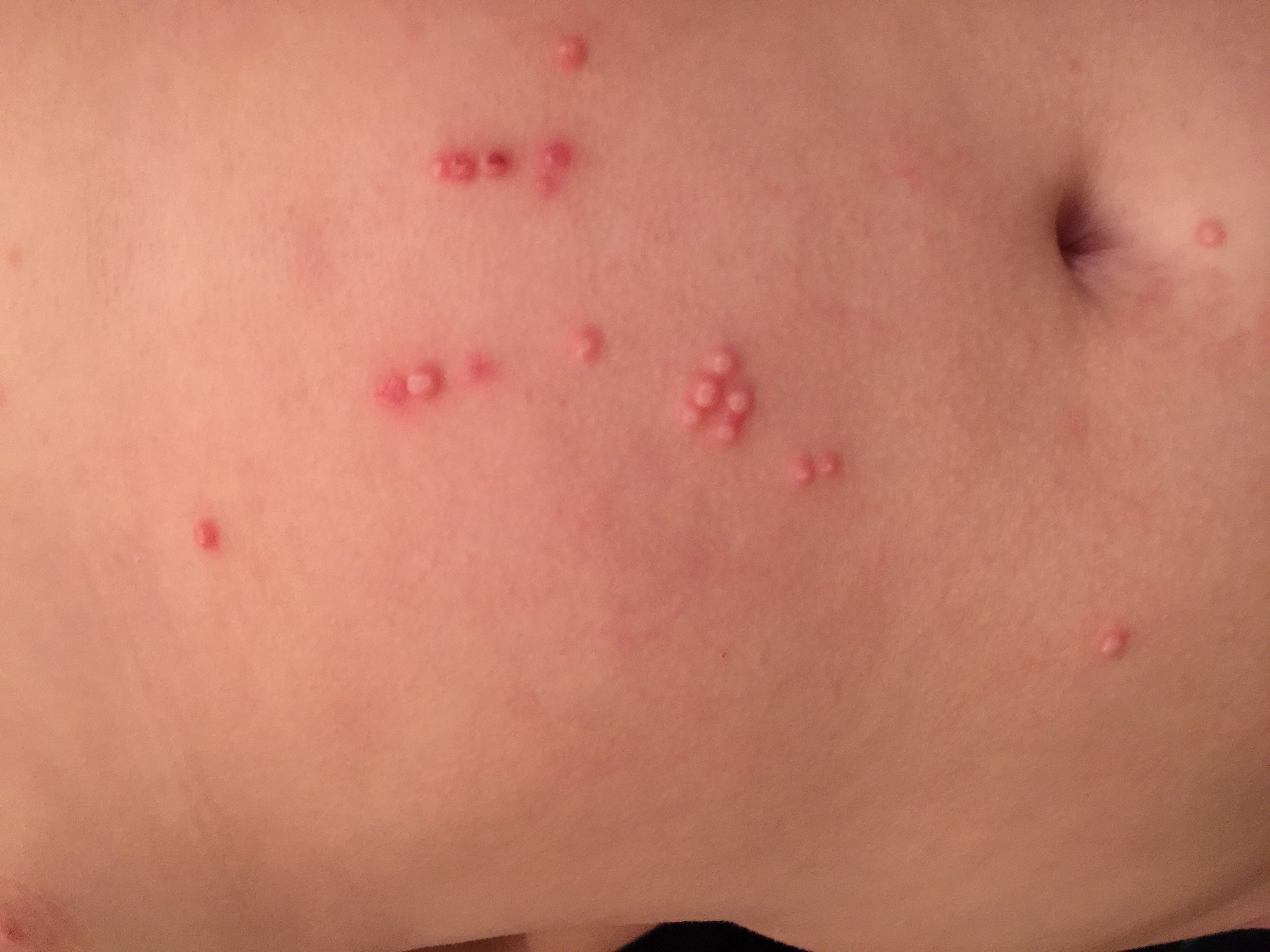
Molluscum Contagiosum: An Overview
Molluscum contagiosum is a common skin infection caused by a poxvirus known as the molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV). This highly contagious condition primarily affects children, adolescents, and sexually active adults. It manifests as small, painless lesions or bumps on the skin that can occur anywhere on the body.
What is Molluscum Contagiosum?
Molluscum contagiosum is a viral infection characterized by the appearance of raised, pearly white, and flesh-colored nodules on the surface of the skin. Though typically harmless and self-limiting, it can be unsightly and irritating, leading individuals to seek treatment for aesthetic reasons.
Who Gets Molluscum Contagiosum?
Molluscum contagiosum can affect individuals of any age, but certain groups are more at risk:
- Children: Most commonly affects school-aged children due to close contact with each other.
- Teenagers and Adults: Particularly those who are sexually active, as the virus can be transmitted through skin-to-skin contact.
- Individuals with Weakened Immunity: People with compromised immune systems may experience more extensive and persistent lesions.
How Common is Molluscum Contagiosum?
While the exact prevalence is challenging to determine, molluscum contagiosum is relatively common worldwide. It is a frequent dermatologic complaint in pediatric and sexual health clinics.
Symptoms and Causes
What are the Signs of Molluscum Contagiosum?
Signs and symptoms typically appear a few weeks to a few months after exposure to the virus, including:
- Small, Dome-shaped Papules: These are firm, round, and flesh-colored bumps with a dimpled center.
- Size and Distribution: Lesions can range from 1 to 5 millimeters in diameter and can appear singly or in clusters.
- Painless but Itchy: The nodules are generally painless, though they may become itchy, red, or swollen if irritated.
Causes and Transmission
The molluscum contagiosum virus spreads through:
- Direct Skin-to-Skin Contact: This is the most common method of transmission.
- Fomite Transmission: Virus can spread through contact with contaminated objects like towels, clothing, or toys.
- Sexual Contact: In adults, lesions may appear in the genital area, and the infection can be transmitted sexually.
Diagnosis and Tests
How is Molluscum Contagiosum Diagnosed?
Diagnosis is typically made by visual examination of the skin lesions. In some cases, a biopsy or scraping may be conducted to confirm the diagnosis, especially if the appearance is atypical.
Management and Treatment
How is Molluscum Contagiosum Treated?
In many cases, molluscum contagiosum resolves without treatment over six to twelve months. However, treatment options are available for quicker resolution and to prevent the spread of the virus.
- Physical Removal: Includes cryotherapy, curettage, or laser therapy; these methods physically remove the lesions.
- Topical Treatments: Include application of antiviral or keratolytic medications. Options are:
Home Remedies and Precautions
- Avoid Scratching: To prevent irritation and spreading, refrain from scratching the affected area.
- Hygiene Practices: Maintain good personal hygiene and avoid sharing personal items like towels or clothing.
Over-the-counter Treatments
Though several products claim to treat molluscum contagiosum, medical consultation is advised before using any OTC options.
Prevention
How Can I Prevent Molluscum Contagiosum?
- Maintain Good Hygiene: Regular washing of hands and body.
- Avoid Sharing Personal Items: Towels, razors, and clothing should not be shared.
- Limit Skin Contact: Prevent direct contact with infected individuals' skin lesions.
- Use Protection During Sexual Activity: For sexually active individuals, using protection can help prevent the spread of lesions in the genital area.
Outlook / Prognosis
Can Molluscum Contagiosum Come Back?
The infection may recur, especially if the initial lesions were not completely resolved or if the individual is re-exposed to the virus.
Living With Molluscum Contagiosum
- Monitor Lesions: Keep an eye on existing lesions for changes in appearance.
- Seek Medical Advice: If lesions persist, spread rapidly, or become inflamed, consult a healthcare provider.
When Should I Call the Doctor?
Contact a healthcare provider if:
- The lesions do not improve or clear after several months.
- You have a weakened immune system.
- Lesions are located on sensitive areas like the face or genitals.
- There are signs of bacterial infection such as increased redness, swelling, or pus.
Understanding molluscum contagiosum and adhering to preventive measures can help manage and reduce the spread of this common skin infection. Medical consultation is advised for appropriate diagnosis and to explore suitable treatment options.
Identify Skin Conditions Instantly
Try Rash ID for Free