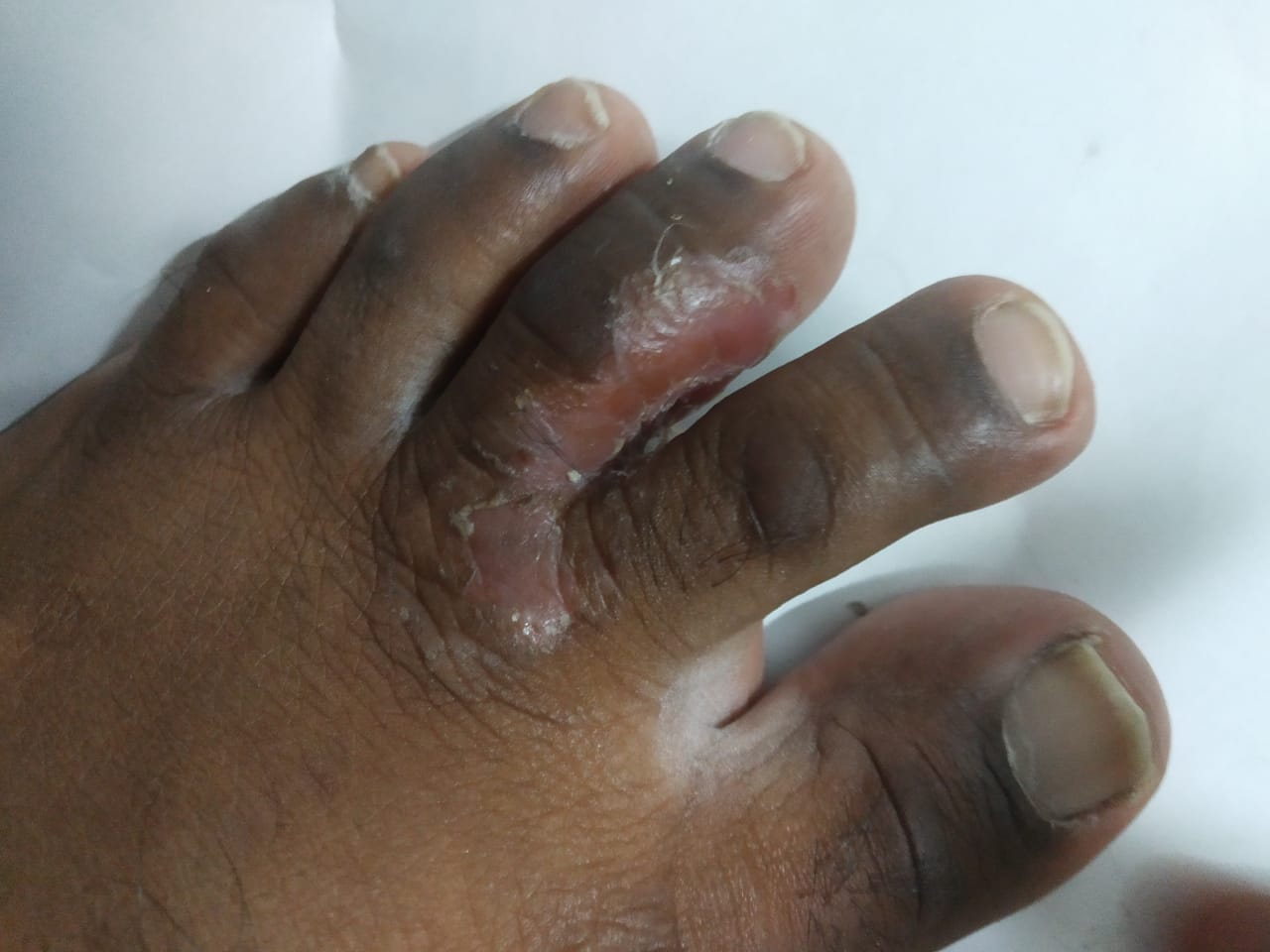
Tinea Pedis (Athlete's Foot)
What is Tinea Pedis?
Tinea pedis, commonly known as "athlete's foot," is a contagious fungal infection caused by dermatophytes, a group of fungi that thrive in warm, moist environments. This condition primarily affects the skin on the feet, particularly between the toes. Despite its name, you don't have to be an athlete to suffer from athlete's foot. The infection is prevalent among people who frequently wear closed footwear and frequent damp areas such as lockers and public showers.
Types of Tinea Pedis
Tinea pedis can present itself in several variations, each with distinct characteristics. Here are the types:
- Interdigital (Toe Web) Infection: The most common type, which occurs between the toes, usually the fourth and fifth. It is characterized by itching, burning, and peeling skin.
- Moccasin Type: This type involves the sole and heel of the foot and may extend to the sides. It causes scaly and dry skin, and sometimes it can cause thickened skin.
- Vesicular Type: In this form, the infection results in the formation of blisters that can be itchy and painful.
- Ulcerative Type: Less common, this type involves painful erosions primarily seen in individuals with weakened immune systems.
How to Recognize Tinea Pedis: Common Symptoms and Visual Clues
Recognizing tinea pedis is vital for early and effective treatment. Here are some ways to identify the condition:
- Itching and Burning: A persistent, often intense itchiness and a burning sensation are classic symptoms.
- Cracked, Peeling Skin: Peeling skin, especially between the toes, is a common occurrence.
- Redness and Inflammation: Affected areas often appear red and may become swollen.
- Blisters: In the vesicular type, blisters filled with fluid may form.
- Thickened Skin: Particularly in the moccasin variant, the skin on the soles may thicken and appear scaly.
Who Gets Tinea Pedis?
Certain factors increase the risk of developing tinea pedis:
- Walking barefoot in public showers, gyms, or swimming pools.
- Wearing tight, non-breathable shoes or socks.
- Having sweaty feet.
- Living in a warm climate.
- Having a weakened immune system.
How Common is Tinea Pedis?
Tinea pedis is highly prevalent, affecting an estimated up to 15% of the global population at any time. It is particularly common in adults, although it can affect children as well.
Symptoms and Causes
What Causes Tinea Pedis?
Fungi known as dermatophytes that naturally reside on human skin cause tinea pedis. These fungi proliferate in moist environments, leading to infection when conditions are favorable.
How Contagious is Tinea Pedis?
Tinea pedis is highly contagious. It can be spread through direct contact with the infected area or by touching contaminated surfaces, clothing, shoes, and towels.
Diagnosis and Tests
How Is Tinea Pedis Diagnosed?
Diagnosis generally involves a physical examination of the affected skin by a healthcare provider. In some cases, skin samples may be taken for microscopic examination or fungal culture to confirm the diagnosis.
Management and Treatment
How Is Tinea Pedis Treated?
Tinea pedis is treatable with both over-the-counter and prescription antifungal medications. Treatment usually involves topical applications, but oral medications may be prescribed for severe cases.
Antifungal Creams and Powders
Over-the-counter antifungal treatments are often effective. Common OTC options include:
- Clotrimazole (Lotrimin®)
- Miconazole (Micatin®)
- Terbinafine (Lamisil AT®)
- Tolnaftate (Tinactin®)
These should be applied as directed for at least 1 to 2 weeks after the symptoms disappear.
Oral Medication
In cases where topical applications fail, or for widespread infections, oral antifungals may be prescribed, such as:
- Terbinafine (Lamisil®)
- Itraconazole (Sporanox®)
- Fluconazole (Diflucan®)
Home Remedies for Tinea Pedis
While medical treatments are preferred, some home remedies may offer relief:
- Soaking feet in a saline solution or diluted vinegar to create an inhospitable environment for the fungus.
- Keeping feet dry and changing socks frequently.
Steroid Creams
Corticosteroid creams can alleviate inflammation, but they should not be relied upon as the sole treatment for fungal infections.
What Cures Tinea Pedis?
Consistent and complete adherence to the antifungal treatment is crucial for curing tinea pedis.
Prevention
How Can I Prevent Tinea Pedis?
Key preventive measures include:
- Wearing flip-flops in communal areas like showers and pools.
- Keeping feet dry and changing socks regularly.
- Using antifungal powders if you are prone to sweating.
- Avoiding shared towels, socks, and footwear.
Outlook / Prognosis
Can Tinea Pedis Come Back?
Yes, recurrence is possible, particularly if preventive measures aren't taken or treatment is not completed.
Living With
When Should I Call the Doctor?
Seek medical advice if:
- The condition persists despite treatment.
- You notice signs of secondary bacterial infection, such as increased redness, pus, or swelling.
- You have diabetes and suspect tinea pedis.
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor?
- What is the best treatment for my infection?
- Are there lifestyle changes I can make to prevent recurrence?
- Should I avoid certain activities until my foot heals?
Additional Common Questions
Can Tinea Pedis Affect My Nails?
Yes, untreated tinea pedis can spread to toenails (onychomycosis), leading to thickened, discolored nails that are harder to treat.
Can Tinea Pedis Spread to Other Parts of the Body?
Athlete's foot can spread to other body parts, including the hands if touched, or to other areas if the fungi are spread via towels or clothing.
For further information, please refer to the following resources:
Identify Skin Conditions Instantly
Try Rash ID for Free